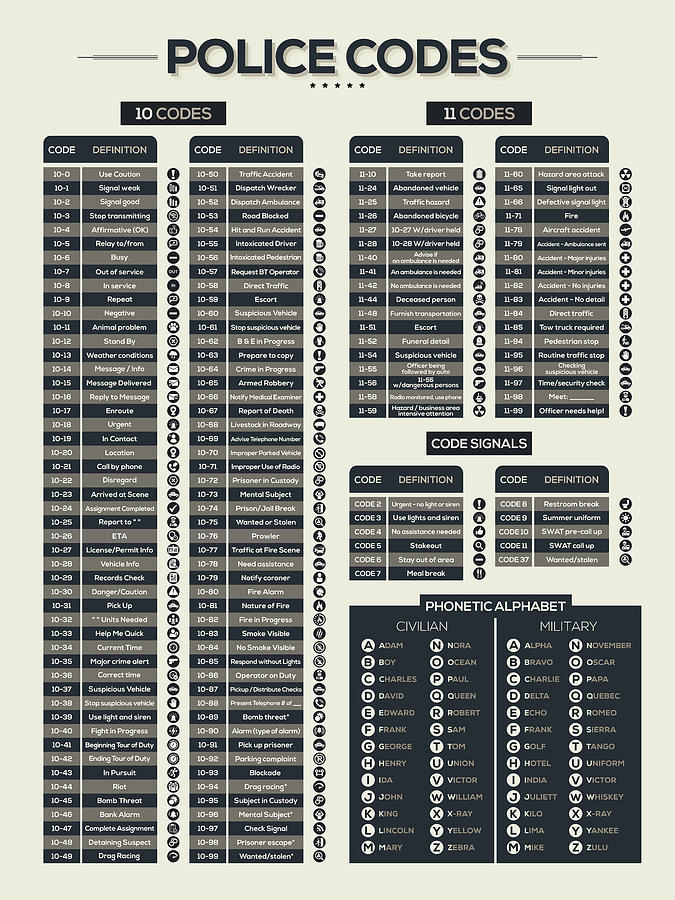
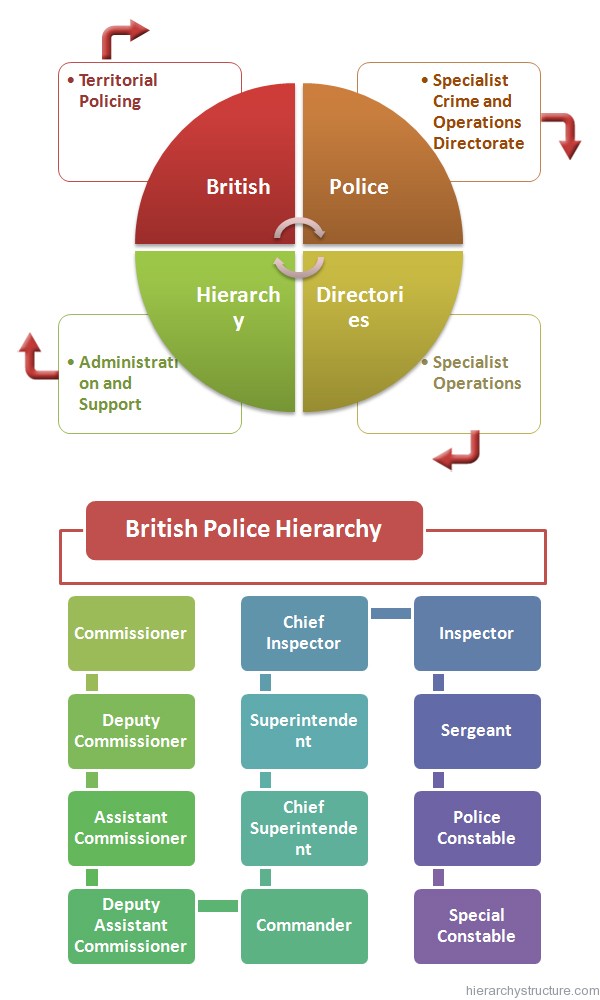
When it comes to understanding the role and structure of police forces worldwide, we're diving into a massive topic that affects every corner of the globe. Imagine this: police officers are the backbone of public safety in nearly every country, but their roles, responsibilities, and structures vary wildly depending on where you are. Whether you're in the bustling streets of Tokyo or the serene villages of rural Kenya, police forces play a crucial role in maintaining order and protecting communities. But what do they actually do? And how do their perspectives shape the way they operate?
Let's face it, policing is one of the most debated and misunderstood topics out there. While some see police as the ultimate protectors, others view them as enforcers of authority. But what about the police themselves? What do they think? Recently, a study revealed that 40% of police officers around the world have unique perspectives on their roles, challenges, and the systems they operate in. This is a game-changer because it sheds light on the human side of policing.
So, if you're curious about how police forces function globally, why they differ so much, and what 40% of police officers have to say about their jobs, you're in the right place. Buckle up, because we're about to break it all down for you in a way that's easy to digest but packed with insights. Let's get started!
Read also:Perdita Weeks Health Journey Overcoming Challenges With Grace
Table of Contents
- Overview of Police Forces Worldwide
- A Brief History of Policing
- Structure of Police Forces
- Key Roles of Police Officers
- 40% of Police Perspectives: What They Think
- Challenges Faced by Police Forces
- Technology in Policing
- Training and Development
- The Future of Policing
- Conclusion
Overview of Police Forces Worldwide
Police forces around the world are as diverse as the countries they serve. In some places, you have highly centralized systems, like in France, where the national police operate under a single authority. In others, like the United States, policing is decentralized, with local departments handling their own jurisdictions. But regardless of the structure, the core mission remains the same: to maintain law and order, protect citizens, and prevent crime.
However, the way police forces achieve these goals can vary significantly. For instance, in countries with high crime rates, police might focus more on enforcement and deterrence. Meanwhile, in nations with lower crime rates, police may emphasize community engagement and prevention. This diversity in approach is what makes the global policing landscape so fascinating—and complex.
Key Differences in Policing Around the World
Let’s break it down a bit further. In countries like Japan, where community policing is king, officers spend a lot of time building relationships with locals. They know the names of shopkeepers and residents, and they often walk their beats to stay connected. On the flip side, in places like Brazil, where violence and drug-related crimes are rampant, police may rely more on military-style tactics to maintain control. It's all about adapting to the local context.
Here’s a quick snapshot of how policing differs across continents:
- North America: Decentralized systems with a focus on technology and community policing.
- Europe: Centralized systems with an emphasis on human rights and legal frameworks.
- Asia: A mix of centralized and decentralized models, with a strong focus on maintaining public order.
- Africa: Challenges include underfunding and corruption, but community-based approaches are gaining traction.
- Australia and Oceania: Policing is heavily influenced by indigenous perspectives and cultural sensitivity.
A Brief History of Policing
Before we dive deeper into the role and structure of police forces, it’s important to understand where they came from. The concept of policing as we know it today dates back to the 19th century, when Sir Robert Peel established the Metropolitan Police Service in London in 1829. Peel’s principles, which emphasized professionalism, accountability, and community trust, laid the foundation for modern policing.
Over time, policing evolved to meet the needs of changing societies. In the 20th century, technological advancements like radios and cars revolutionized how officers operated. Today, with the rise of digital technology, police forces are adapting once again to tackle cybercrime, surveillance, and data analysis.
Read also:Ree Drummond The Pioneer Womans Life Career And Influence
The Evolution of Police Roles
From foot patrols to high-tech surveillance, the role of police has shifted dramatically over the years. Here’s a quick timeline:
- 19th Century: Establishment of professional police forces in major cities.
- 20th Century: Introduction of cars, radios, and forensic science.
- 21st Century: Focus on community policing, technology, and global cooperation.
Structure of Police Forces
Now, let’s talk about how police forces are structured. Depending on the country, police may operate under national, regional, or local authorities. In some places, like Germany, you’ll find both federal and state police forces working together. In others, like the UK, local police forces handle most day-to-day operations while national agencies focus on more complex issues like terrorism and organized crime.
But it’s not just about who’s in charge. The structure of police forces also affects how they interact with the public. For instance, in countries with centralized systems, officers may have more resources and training, but they might also be seen as distant or unapproachable. In decentralized systems, officers are often more connected to their communities, but they may face challenges like limited funding and resources.
Key Components of Police Structure
Here are some of the main components you’ll find in most police forces:
- Patrol Officers: The frontline workers who respond to calls and maintain order.
- Investigative Units: Teams that handle complex cases like homicide, fraud, and cybercrime.
- Command Staff: The leaders who oversee operations and make strategic decisions.
- Support Staff: Professionals like dispatchers, analysts, and administrative personnel.
Key Roles of Police Officers
So, what exactly do police officers do? Their roles can vary depending on their rank, department, and location, but there are some common responsibilities that most officers share. At the core, police officers are tasked with enforcing laws, protecting citizens, and preventing crime. But their day-to-day duties can range from responding to emergencies to conducting community outreach programs.
Here’s a closer look at some of the key roles:
- Crime Prevention: Officers patrol neighborhoods to deter criminal activity.
- Investigation: They gather evidence, interview witnesses, and solve crimes.
- Community Engagement: Building trust and cooperation with local residents.
- Emergency Response: Handling crises like accidents, natural disasters, and acts of violence.
40% of Police Perspectives: What They Think
Now, here’s where things get interesting. Recent studies have shown that 40% of police officers worldwide have unique perspectives on their roles and challenges. These officers often feel that their work is misunderstood by the public, and they believe that more needs to be done to address issues like mental health, training, and community relations.
For example, many officers emphasize the importance of empathy and communication in their daily interactions. They believe that building trust with the community is just as important as enforcing laws. Others highlight the need for better resources and support, especially in high-risk areas.
Challenges Faced by Police Forces
Of course, no discussion about policing would be complete without addressing the challenges. Police forces around the world face a host of issues, from underfunding and corruption to public distrust and burnout. In some countries, officers are overworked and underpaid, leading to high turnover rates and morale problems. In others, systemic issues like racism and bias continue to plague the profession.
But it’s not all doom and gloom. Many police forces are actively working to address these challenges through reforms, training programs, and community initiatives. For instance, some departments have implemented body cameras to increase transparency and accountability. Others are focusing on mental health support for officers, recognizing the toll that the job can take on their well-being.
Top Challenges According to 40% of Officers
Here’s what 40% of police officers say are the biggest challenges they face:
- Public Distrust: Building trust with communities is a top priority.
- Resource Constraints: Many departments lack the funding and equipment they need.
- Mental Health: Officers struggle with stress, trauma, and burnout.
- Systemic Issues: Addressing bias, racism, and corruption within the system.
Technology in Policing
Technology has transformed the way police forces operate in recent years. From body cameras and drones to AI-powered analytics and facial recognition systems, officers now have access to a wide range of tools to help them do their jobs more effectively. But with these advancements come new challenges, such as privacy concerns and the potential for misuse.
For instance, while body cameras can increase transparency and accountability, they also raise questions about data storage and access. Similarly, AI-powered systems can help predict crime patterns, but they may also perpetuate biases if not carefully designed and monitored.
The Future of Tech in Policing
Here’s a glimpse of what the future might hold:
- AI and Machine Learning: Used for predictive policing and data analysis.
- Drone Technology: For surveillance and search-and-rescue operations.
- Blockchain: To ensure secure and transparent record-keeping.
Training and Development
Training is a critical component of policing, and it’s something that 40% of officers believe needs improvement. Many departments are now focusing on areas like de-escalation techniques, cultural sensitivity, and mental health awareness. The goal is to equip officers with the skills they need to handle a wide range of situations, from routine traffic stops to high-stakes emergencies.
But training doesn’t stop after graduation from the academy. Officers need ongoing professional development to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies. This includes everything from cybersecurity to crisis intervention.
Key Areas of Training
Here are some of the key areas where officers receive training:
- Use of Force: Learning when and how to use weapons and physical force.
- De-Escalation: Techniques for calming tense situations without violence.
- Cultural Competency: Understanding and respecting diverse communities.
The Future of Policing
As we look to the future, it’s clear that policing will continue to evolve in response to changing societal needs and technological advancements. The focus will likely shift towards more community-oriented approaches, with an emphasis on collaboration, trust, and accountability. At the same time, officers will need to adapt to new challenges like cybercrime and global terrorism.
One thing is certain: the role of police forces worldwide will remain crucial in maintaining public safety and order. By addressing the challenges they face and embracing new technologies and training methods, police can continue to serve their communities effectively and with integrity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the role and structure of police forces worldwide is essential for anyone interested in public safety and governance. From the diverse approaches to policing across continents to the unique perspectives of 40% of officers, there’s so much to learn and explore. By addressing challenges like public distrust, resource constraints, and systemic issues, police forces can continue to improve and evolve.
So, what can you do? Start by staying informed and engaged. Share this article with others, leave a comment with your thoughts, or explore more content on our site. Together, we can work towards a safer, more just world. Thanks for reading, and let’s keep the conversation going!